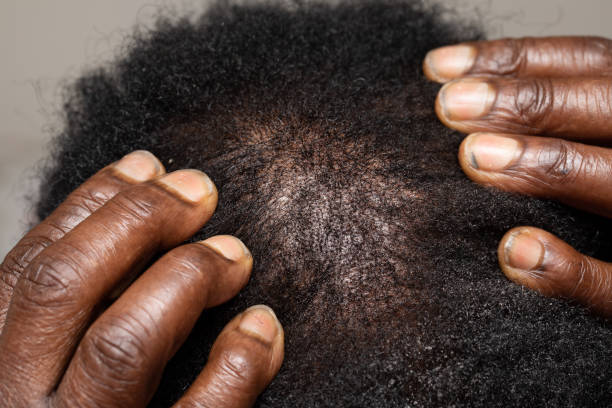
Hair loss in men, also known as male-pattern baldness or androgenic alopecia, is influenced by various factors. They are
1. Heredity/Aging
- Genetics play a significant role in male-pattern baldness. If baldness runs in your family, you are more likely to experience it.
- With age, hair growth slows, and hair follicles shrink, producing finer and shorter hair. This is often a gradual process, starting at the temples or crown.
2. Severe Physical/Emotional Stress
- Stressful events, such as surgery, illness, or psychological trauma, can trigger a condition called telogen effluvium, where hair prematurely enters the shedding phase.
- Emotional stress, though less common, can also exacerbate existing hair loss conditions.
3. High Fever or Severe Infection
- Illnesses like the flu, COVID-19, or any condition causing prolonged fever can disrupt the hair cycle.
- After recovery, hair typically regrows, although it might take several months.
4. Poor Diets (Lacking Enough Protein)
- Nutritional deficiencies, particularly in protein, iron, zinc, and vitamins like D and B12, can weaken hair and slow its growth.
- Crash diets or eating disorders like anorexia can also lead to hair loss.
5. Thyroid Disease
- Both hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) and hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) can disrupt the hormonal balance needed for hair growth, leading to thinning or shedding.
6. Nervous Habits (Trichotillomania)
- Trichotillomania is a psychological condition where individuals compulsively pull out their hair, causing patchy baldness.
- This behavior is often linked to anxiety or stress.
7. Radiation Therapy
- Radiation aimed at the scalp can damage hair follicles, causing hair loss that may be temporary or permanent, depending on the dosage and area treated.
Additional Factors to Consider
In addition to the above causes, other contributing factors include:
- Hormonal Changes: Elevated levels of dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a byproduct of testosterone, shrink hair follicles in genetically predisposed men.
- Medications and Treatments: Drugs used to treat cancer, arthritis, depression, or high blood pressure can have side effects, including hair loss.
- Scalp Infections: Conditions like ringworm can cause temporary hair loss if left untreated.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system attacks hair follicles.
- Lifestyle Factors: Smoking and alcohol use may accelerate hair loss by reducing blood flow and nutrients to hair follicles.
Understanding the underlying cause is essential for managing hair loss. Early consultation with a healthcare professional or dermatologist can help in diagnosing the cause and finding an appropriate treatment.
For even more hair care tips and insights, follow us on Instagram here and check out our Facebook page here. We post additional content that you don’t want to miss.